Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nagatake, Taku; Kunugi, Tomoaki*; Takase, Kazuyuki
Dai-24-Kai Suchi Ryutai Rikigaku Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (USB Flash Drive), 4 Pages, 2010/12
GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) has been developed for drawing system in computer. In order to achieve the high-performance computing for rendering high-quality 3D graphics, the GPU has many processing units and the wide memory bandwidth. Nowadays, the performance of GPU becomes much higher than that of CPU (Central Processing Unit), so that the attempt to make use of GPU for the science calculation and general purpose is performed: This attempt is called "GPGPU" (General Purpose GPU) or "GPU computing". Now we are developing MARS (Multi-interfaces Advection and Reconstruction Solver) (1) with GPU. The MARS is one of the surface volume tracking methods for multi-phase flows. In this paper, the performance of GPU is compared to the CPU. And the parallelized method for the multi-GPU system is considered.
Ito, Kei; Kunugi, Tomoaki*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Dai-24-Kai Suchi Ryutai Rikigaku Shimpojiumu Koen Rombunshu (USB Flash Drive), 5 Pages, 2010/12
In the design study of a large-scale sodium-cooled fast reactor in Japan (JSFR), an innovative concept with a compact reactor vessel and resulting higher coolant velocity in the vessel has been examined. Such a concept may causes several thermal-hydraulics issues in the reactor vessel. One of very important issues is the cavitation phenomena due to a sub-surface vortex caused near the suction mouth of an outlet pipe. For the structural integrity, the cavitation phenomena have to be suppressed. However, the onset condition of the cavitation phenomena can not be clarified easily because the cavitation phenomena shows highly complicated behaviors associated with phase change. Therefore, the authors are developing a high-precision numerical simulation scheme for vortical flows to simulate the cavitation phenomena accurately and efficiently. In this paper, a high-precision numerical simulation scheme for vortical flows is developed and a basic verification of the scheme is conducted.
Shirai, Koichiro*; Ishii, Katsuya*; Ishigaki, Masahiro
no journal, ,
Taconis oscillations, which are spontaneous oscillations of a gas column in a tube with cold and hot walls, are studied numerically. We use axisymmetric compressible Navier-Stokes equations. The spontaneous oscillations are observed in the closed tube when the temperature ratios of hot part to cold part 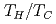 are more than a critical value. We observed three types of oscillation modes when the length ratios of hot part to cold part
are more than a critical value. We observed three types of oscillation modes when the length ratios of hot part to cold part 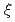 is 0.3. The oscillation states of fundamental mode and second mode are observed in the region upside the critical temperature ratios of Rott's theory.
is 0.3. The oscillation states of fundamental mode and second mode are observed in the region upside the critical temperature ratios of Rott's theory.
Yamashita, Susumu; Yonemoto, Yukihiro; Yamada, Tomonori; Kunugi, Tomoaki*; Muramatsu, Toshiharu
no journal, ,
Quantitative evaluation and controlling the residual stress which is induced by laser welding is of important problemfor a life extension of FBRs (Fast Breeder Reactors) and the guarantee of the reliability of the repair processes. Numerical simulation is an effective tool for deep understanding of their problems and it needs to have high accuracy, robustness and reliability. We have recently constructed the fully parallelized laser welding simulation code which satisfies above aspects using some advanced numerical models. Concretely, VSIAM3 (Volume and Surface Integrated Average based Multi Moment Method) numerical model as the spatial discretization, an efficient free surface capturing scheme, THINC scheme, and FAVOR method as the solid phase expression has been applied to the code. We have conducted modest large-scale laser welding simulations by using a supercomputer in Japan Atomic Energy Agency and obtained some preliminary results. And reasonable results were obtained.